Deep thinking or reasoning has become a hot topic in the AI chatbot world lately, with most bots now offering the ability to “think” before responding. But when should you actually use this feature? Sure, the AI can think (deeply) before answering anything, but that doesn’t mean it should. Let’s break down when to use deep think mode and when the regular mode will do the trick.
What is AI Reasoning Mode?
AI reasoning mode allows AI chatbots to tackle a prompt through a structured, step‑by‑step process rather than directly providing the most statistically likely answer. The model simulates breaking your question into a series of intermediate reasoning steps that help guide the final response. This process dramatically reduces the risk of errors or AI hallucinations.
At its core, reasoning mode uses chain‑of‑thought prompting, instructing the AI to “think aloud” by spelling out every intermediate calculation, fact‑check, or logical inference. This walkthrough process ensures each piece of information is validated before the chatbot delivers its conclusion.
To give you an example, I asked Deepseek, with DeepThink enabled, a simple subtraction question “If John has 5 apples and gives 2 to Mary, how many does he have left?“. In the screenshot below, you can see the detailed thinking process it used to ensure the answer is correct to such a simple question.
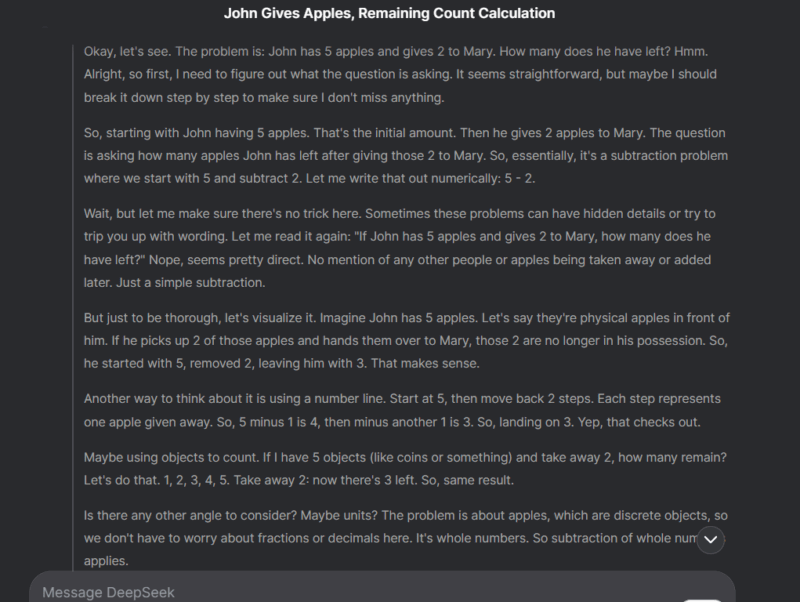
When Not to Use the Reasoning Mode
Before discussing when to use reasoning mode, it’s important to understand that for many routine questions, the simpler mode is sufficient. For most day-to-day questions, the reasoning mode doesn’t bring anything special to the table. In fact, it slows down the process, uses unnecessary server/token resources, and may provide bloated answers to simple questions.
There’s no need to enable reasoning mode for common questions like simple definitions, factual information, basic conversions, and yes/no queries. For such straightforward requests, using reasoning mode would be unreasonable, as they don’t require any complex reasoning at all.
Always enabling reasoning mode will lead to long delays for simple answers and eat up your plan’s limits (if any). Not to mention, it also puts extra pressure on the AI chatbot’s servers for no real benefit. For example, DeepSeek often gives a “server busy” error under load if you have DeepThink (R1) enabled but works fine when you disable it.
Related: Other than deep thinking, it is also important to give it a clear prompt so it understands what you really want to ask. Here are some expert tips to craft the perfect AI prompts.
When to Use the Reasoning Mode
The reasoning mode really shines when the queries have no obvious/factual answer, usually because of multiple variables at play. The reasoning mode can break down such queries and provide a compelling answer. Furthermore, most complex questions with multiple details also benefit from step-by-step reasoning.
To help you understand better, below I am listing some common queries that benefit from reasoning mode enabled:
- Complex problem-solving: reasoning helps with math, coding, or engineering problems that have multiple variables and dependencies. For example, “find the derivative of f(x) = (3x² + 2x) / ln(x)“.
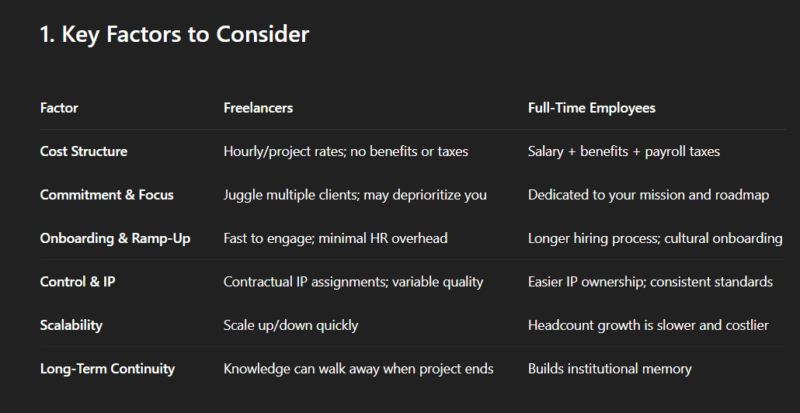
- Strategic decision-making: decisions that involve trade-offs involve weighing pros/cons and forecasting outcomes. Reasoning mode can minimize the chances of incorrect assumptions and hallucinating facts. An example prompt could be “Is it better to hire freelancers or full-time employees for a startup’s MVP development?“.
- Technical troubleshooting: while regular mode may be fine for common software problems, you’ll need reasoning mode enabled for complex software and mechanical problems. Especially, if the cause is unknown.
- Creative brainstorming: prompts for brainstorming new ideas usually involve factoring in multiple variables to generate unique ideas. Reasoning steps ensure all variables are properly factored in for creative ideas. For example, the prompt “Suggest 10 unique plot twists for a sci-fi novel about AI” will benefit from reasoning to avoid overlapping or dull ideas.
- Hypothetical scenarios: exploring “what if” scenarios can benefit from reasoning as it involves simulating outcomes based on different assumptions. An example prompt could be “How would a 4-day workweek impact productivity in a tech company?“.
Apart from handling complex prompts better, the reasoning process also helps the user understand and validate how the AI arrived at the answer. Most AI chatbots show the reasoning steps they took (might need to manually reveal them), and the user can review the steps to learn the AI’s thinking process ensuring the AI didn’t make a mistake.
Choosing the right mode for your AI queries will ensure you get the right answer without wasting time or resources. You can also copy/paste the same query in separate chats to see which mode provides the best answer. While you are at it, make sure you take advantage of these hacks to produce better results.