If you have ever tried to troubleshoot internet issues – such as slow Wi-Fi – you’ve likely run an internet speed test. These tests measure several metrics with varying values, which can be confusing at first. If you’re struggling to interpret your speed test results, this guide will tell you everything you need to know.
Understanding the Download and Upload Speeds
Download and upload speeds are the two main parameters that determine the speed of your overall internet connection. Both represent different states of data transfer and impact different online activities.
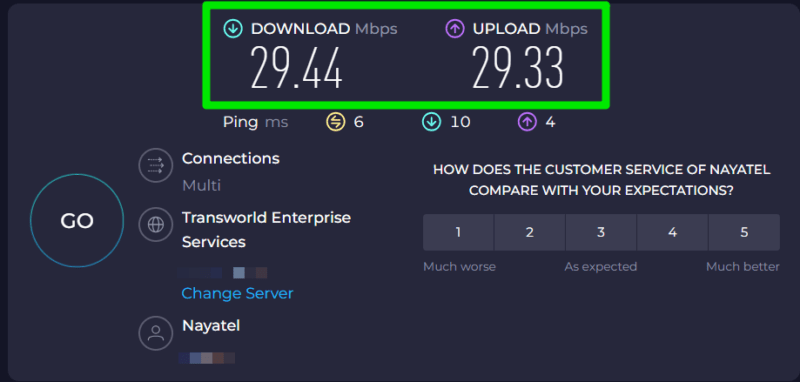
Download Speed
Download speed determines how fast your device can pull data from the internet. It’s measured in Mbps (megabits per second) and affects all online activities that involve sending data toward you, such as streaming media, web browsing, downloading files, etc.
Most activities have a recommended download speed requirement, which usually ranges from 5-25 Mbps. Higher speeds will lead to faster downloading of files and the ability to run multiple internet activities simultaneously. You can check our guide on how fast internet connection you need to learn what speeds you need for different activities.
Upload Speed
Upload speed determines how fast your device can send the data to the internet. It’s also measured in Mbps, but it affects activities that involve taking data from your device to the internet, such as video conferencing, cloud backups, live streaming, etc.
While demands for download and upload speed are similar depending on activity, the upload speed is usually slower than the download speed if you have a DSL or cable connection. While a fiber connection generally has the same download/upload speeds, it’s still worth confirming before getting a connection.
It’s important to know that the Mbps speed you see in speed tests is not the same as MBps (megabytes per second). The small case ‘b’ in Mbps refers to “megabits” while the capital ‘B’ in MBps refers to “megabytes”. 1 byte is equal to 8 bits. Mbps measures speed, while MB is used to measure file sizes. For example, 100 Mbps doesn’t mean you’re transferring 100 MB of data per second. It’s actually around 12.5 MB per second (100/8 = 12.5MBps) for downloads and uploads. To learn more, check our guide on the difference between megabits and megabytes.
What is Ping and Why It’s Not Important
Ping, also called latency, is basically the reaction time of your internet connection measured in milliseconds (ms). It’s the total time your network takes to send and receive data from the server.
When you run a speed test, it also tests your ping by sending a small packet (ICMP echo request) to the server and then receiving the echo reply. The total time taken for this round trip is your total ping.
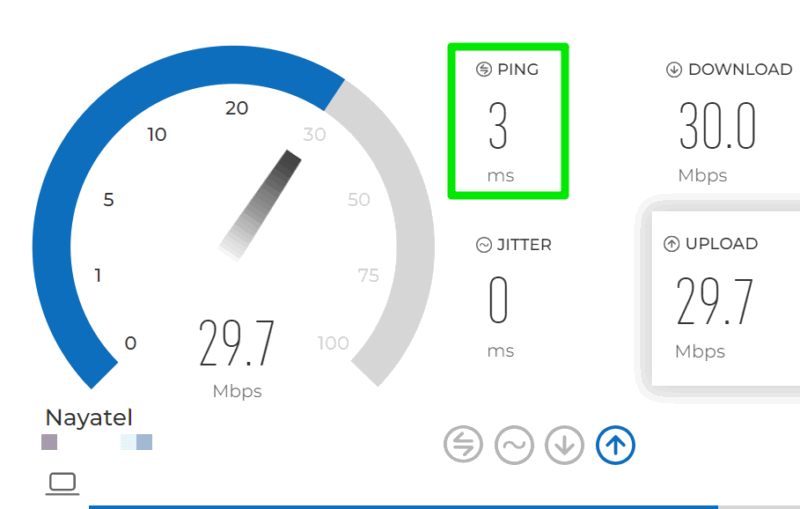
In reality, the ping value you see in a speed test is useless, since it often connects to the nearest server to run the speed test. In regular use, you will connect to different parts of the world on different websites, which will change the ping value.
If you are seeing high ping in a game/app while your ping is fine in the speed test, it is probably because the server is located too far from you and there could be issues with the route your ISP is taking to connect to that specific server.
Another thing to note is that your ping value is independent of the download/upload speed. A low ping value doesn’t mean your download speed is slow, and vice versa.
Too Much Jitter Is No Good
Alongside ping, you will see a jitter value that is also recorded in milliseconds. It’s an important metric that shows the stability of your connection.
Jitter measures the variation in latency between multiple packets sent and received. Ideally, all packets should complete their round trip at a similar time. The variation between the packet round trip time is called jitter. For example, if one packet takes 100ms to complete the trip and the other takes 110ms, then 10ms is the jitter.
If the jitter value is too high in the speed test, it means the packets are arriving with inconsistent delays. A jitter value below 20ms is considered good for most tasks. At 20-50ms, you will start noticing problems in activities like online games or video calls. Any value above will create problems in ping-dependent activities, making them impractical to use.
What Affects the Speed Test Results?
Speed test results won’t always reflect the exact speeds your ISP promised, there are many factors that can affect the results. Firstly, make sure you are testing correctly. Try connecting using an ethernet cable, close programs that can use the network, and run multiple tests to check average results.

If you are still getting lower speeds, then the type of internet connection is probably the reason, like DSL, cable, fiber, etc. Here’s what you should expect depending on the connection:
- DSL: its speed is affected by the distance between your router and telephone exchange. It’s also prone to congestion during peak hours. Expect 50% to 80% of advertised speeds under normal conditions.
- Cable: since it’s a shared infrastructure, it can lead to slow speeds when multiple people are connected near your place. Expect 80% to 95% of advertised speeds.
- Wireless/Cellular: the speed is affected by distance and obstacles between your router and the cell tower, and network congestion as well. It’s highly variable throughout the day and can be anywhere from 50% to 80% of advertised speeds.
- Fiber: fiber connection will usually show almost the same speeds as your ISP advertised, and it will be very stable for both downloads and uploads. While rare, you may still get lower internet speed on fiber due to secondary reasons.
Other secondary factors like the number of connected devices, Wi-Fi interference, router/modem technology, and server load, all can lead to different speeds than expected. Unless you are getting too low speeds – like 20-30% of advertised — the fluctuations in internet speed are normal.
What Can You Do to Improve Your Internet Speed?
If you are getting lower speeds than expected even when properly testing, it might be an issue at your or your ISP’s end. Here are some things you can do:
- Restart your router/modem. This usually clears temporary issues.
- Inspect the ethernet cable and make sure connectors are secured and there is no damage. For Wi-Fi, test using both 5GHz and 2.4GHz bands to ensure the issue is not related to coverage.
- Update your router firmware. You can also try using a custom router firmware.
- Disable any VPNs or proxies as they can throttle speeds.
- Make sure your IPS isn’t throttling your bandwidth.
- Change servers on the speed test website. Sometimes a server could be overloaded and show incorrect results.
- If there are other devices connected to the same network, they might be affecting the results (even when not using the internet actively). Disconnect all devices and try again.
If nothing works, you might have to talk to your ISP to help you solve the problem.
Wrapping Up
Internet speed tests can not only help see network performance but also diagnose issues at your end because they show results in ideal conditions. For example, if you have a high ping in an online game while speed test results are fine, the problem is probably with your connection to that specific game’s server.
Image credit: Vecteezy. All screenshots by Karrar Haider.