Windows devices use an older sign-in method called NTLM, which is enabled by default. In the event of a malware attack, it can expose your system password to hackers. They can use different kinds of man-in-the-middle attacks to steal your Windows login details. Luckily, you can protect your Windows NTLM credentials from zero day threats using a few simple tweaks in the NTLM settings.
How Windows NTLM Threats Steal Your Passwords
NTLM (NT LAN Manager) is an older authentication method still used on many Windows devices. It works by turning your password into a code (hash) to verify you without sending the password over the network. This is not secure because if your PC is compromised, your login password will be visible to attackers.
Recently in April 2025, security researcher Check Point blogged about NTLM hash disclosure through a vulnerability called “CVE-2025-24054.” According to them, it’s an ongoing cyberattack targeting government and enterprise users in Poland and Romania. Attackers are using different types of man-in-the-middle attacks, including pass-the-hash (PtH), rainbow table, and relay attacks. Their main target is privileged users or administrators.
While NTLM attacks often target enterprises and governments, home users are also vulnerable. Just interacting with a malicious file can leak your system password.
Microsoft did release a security patch for CVE-2025-24054. So it’s always good to keep your Windows system updated to prevent these attacks. Apart from that, there are a few other things you can do.
1. Disable NTLM Authentication through PowerShell
Open PowerShell in administrator mode, and enter the following. You’ll find another question whether you want to modify the targeted SMB Client Configuration. For that, click A.
Set-SMBClientConfiguration -BlockNTLM $true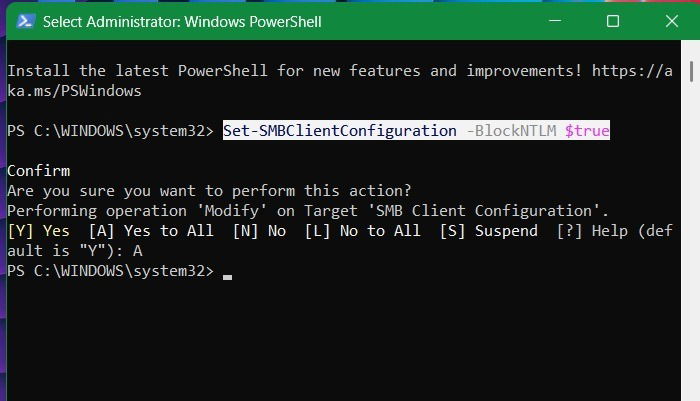
Blocking NTLM over SMB does not affect your latest Windows devices. However, in case, you encounter problems with older printers, NAS servers, or other legacy devices, you can always switch back to allow NTLM over SMB.
Set-SMBClientConfiguration -BlockNTLM $falseThe Server Message Block (SMB) is used for file sharing, and network connections. It is one of the most common connections used by PtH, relay attacks, and other man-in-the-middle attacks. By blocking NTLM over SMB, you’re removing a major gateway for attackers.
2. Disable Older NTLM Protocol in Registry Editor
Many Windows sessions are nowadays hosted in “Kerberos” which is a very secure protocol as it uses ticket-based encrypted authentication. However, there is no need to completely disable NTLM which has many uses. Instead, we will switch to the more secure NTLMv2 protocol instead of NTLMv1.
This can be done from the Registry Editor. First take a backup of your registry. Next, open the Registry Editor in administrator mode, and go to:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa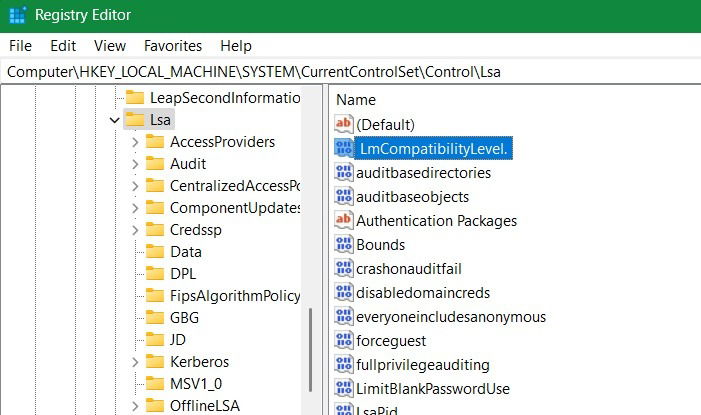
Under the registry key for “Local Security Authority,” (Lsa), go to network security LAN manager authentication level value, “LmCompatibilityLevel.” If it’s not present, create a D-WORD (32-bit) under Lsa as shown above.
Double-click “LmCompatibilityLevel” to open it. You’ll find “0” as the default value. Set it to “3”, “4” or “5” which will set your Windows device to only send NTLMv2 responses, and block all legacy NTLMv1 responses.
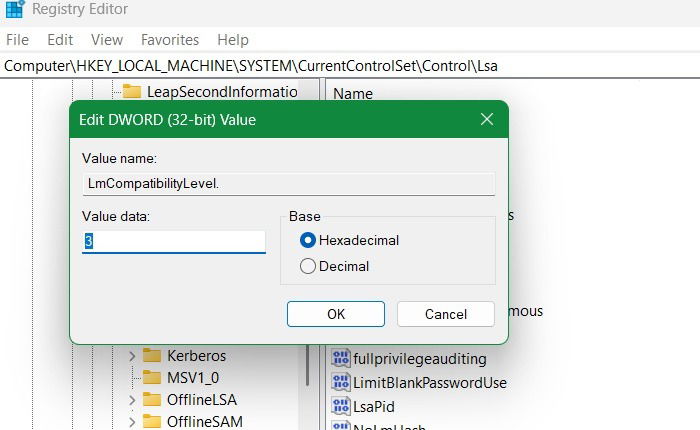
After you do the above change, go to the path below:
COMPUTER\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\ParametersHere, you’ll find a D-WORD value called “RequireSecuritySignature,” or “EnableSecuritySignture”. Its default value should be “1”. If not, then change it to “1.” Once you do it, all future SMB connections would require SMB security signing. This prevents your device credentials from being stolen.
3. Keep Cloud Protection Enabled in Windows Security
The above registry changes are harmless. However, if you don’t want to do them, you can protect your device through a new Windows Security feature that prevents all threats such as phishing attacks emerging online. It can be accessed from Virus & threat Protection -> Manage settings -> Cloud-delivered protection.
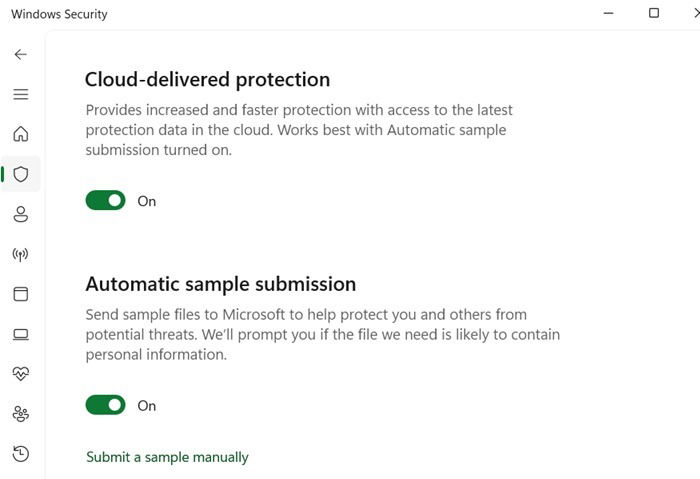
Related: having access to an endpoint protection suite, such as Microsoft Defender, gives you added protection against zero hour threats.
4. Other Security Measures
Microsoft has recommended the following additional security mechanisms to avoid falling victim to NTLM credentials theft:
- Enabling multi-factor authentication: you can enhance your password and PIN-based login security through multi-factor authentication mechanisms. Go to Settings -> Accounts -> Sign-in options. Here, you’ll find many options such as Windows Hello, and creating a physical security key using USB devices.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links: NTLM malware generally spread through malicious links. Although they may get blocked by Windows Security, why take a chance against these remote exploits? Check our detailed guide on how to detect and avoid malicious messages.